MASS FLOW RIG METERING FACILITIES FOR CCS APPLICATIONS AT HERIOT-WATT UNIVERSITY
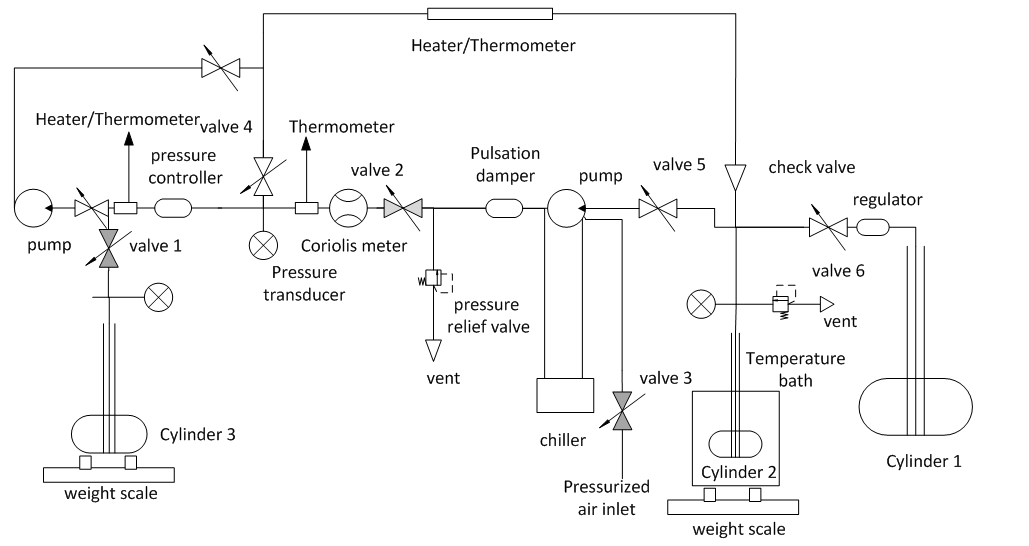
Under the COMET-DECC project, the Centre for Innovation in Carbon Capture and Storage (CICCS) at Heriot-Watt University has designed and developed one of the first kind of a laboratory mass flow rig, as shown in Figure 1, based on gravimetric calibration to investigate the performance of flow meters for deployment in carbon capture and storage. The flow rig can operate in the temperature ranges from 273 to 333 K and at pressures up to 10 MPa. The trials conducted have assessed the accuracy and repeatability of mass flow measurement over a range of pressure, temperature and flow conditions.
In a previously DECC funded project (COMET), we conducted tests using pure dense phase CO2, and demonstrated that in the dense phase pure CO2, Coriolis meter from Krohne can achieve an average measurement accuracy of 0.1% with an experimental measurement error of 0.025% [1, 2]. Due to the unusual thermophysical properties of CO2 streams, various challenges can occur in CO2 transportation and metering systems, including the presence of different type and level of impurities in the captured CO2 stream. This can change the physical properties of captured CO2 stream and consequently the performance of flow meters. Therefore, an assessment of flow meters performance with a range of gas mixtures representative of CCS capture streams needed to be investigated. This investigation was carried out at Heriot-Watt University with industrial partner, Krohne Ltd, in the UKCCSRC – Call 2 project “Performance of Flow Meters with Dense Phase CO2 and CCS Recovery Streams”.
Various CO2 mixtures with impurities, for instance N2, O2, H2 and Ar, representing flow streams from post-combustion, pre-combustion and oxyfuel capture technologies were investigated [3]. The trials then with each mixture were conducted in start / stop operations both in steady state and transient conditions. The experiments were conducted at temperature ranges of 288-295 K, pressure ranges of 1.5-6.1 MPa and mass flow rates of 0.6-32.1 kg/h with turndown ratio between 10 and 50. In each test, the totalised differential mass shown by flowmeter was compared to the mass measured by weighing scale to calculate the test relative deviation. The deviation for the pre-combustion show that it can vary from -2.0 to 2.0 percent with the absolute average deviation of 1.0%, while those for the post-combustion tests varied between -2.0 and 0.7 percent with the absolute average deviation of 1.0%. The deviations of conducted tests with oxyfuel mixtures also varied in the range of -1.8 to 1.8 percent with the absolute average deviation of 1.4% [3]. The analysis of results indicates that the measurements expected to be in agreement with the regulations of EU ETS which require the accuracy within the range of ±1.5% by mass.
For further information, you can contact the project PI, Prof M. Mercedes Maroto-Valer (M.Maroto-Valer@hw.ac.uk) or the project RA, Dr Mahmoud Nazeri (M.Nazeri@hw.ac.uk).

Figure 1. Schematic of the gravimetric mass flow rig [2]
[1] C.-W. Lin, A. Bhattacharji, G. Spicer, and M. M. Maroto-Valer, “Coriolis Metering Technology for CO2 Transportation for Carbon Capture and Storage,” Energy Procedia, vol. 63, pp. 2723–2726, 2014.
[2] C.-W. Lin, M. Nazeri, A. Bhattacharji, G. Spicer, and M. M. Maroto-Valer, “Apparatus and method for calibrating a Coriolis mass flow meter for carbon dioxide at pressure and temperature conditions represented to CCS pipeline operations,” Appl. Energy, vol. 165, pp. 759–764, Mar. 2016.
[3] M. Nazeri, M. M. Maroto-Valer, E. Jukes, Performance of Coriolis Flowmeters in CO2 Pipelines with Pre-combustion, Post-combustion and Oxyfuel Gas Mixtures in Carbon Capture and Storage, Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control, vol. 54, pp. 297–308, 2016.